Course Outline
TEXTBOOK: QuickPass Certified Welding Inspector AWS/CWI Study Guide – based on AWS D1.1 – 2015 edition: This publication deals with Welding Certification and Welding Inspection Exams. Primary emphasis is focused on the Structural Welding Code for Steel.
This is because Welding Inspection involves far more than just looking at welds. A welding inspector must additionally have both a wide range of knowledge and skills and an understanding of the welder’s work.
The Textbook provides both novices as well as experienced welders and inspectors with the information that will assist them in passing the necessary exams.
Code References:
- AWS D1.1 – 2015
- AWS D1.2 – 2014
- AWS D1.3 – 2018
- AWS D1.4 – 2011
- AWS A2.4 – 2012
- AWS A3.0 – 2010
- API 1104 – 2013
This program is useful for anyone taking exams given by the American Welding Society or other agencies that cover:
- Examination
- General Knowledge
- Inspection
- Nondestructive Testing
- Performance
- Process
- Responsibilities
- Safety
- Symbols
- Technology
UPDATED: New Online Testing Environment! (1Year Access)
We proudly announce the release of our new ONLINE Study Center.

ABOUT the TLC ONLINE STUDY CENTER
Gain access to CWI Exam practice questions and specific online content relating to your chosen exam(s). Choose between online chapter reviews, and AWS practice questions, then test your knowledge with simulated timed TLC practice exams.
Use our online chapter reviews, virtual flashcards, and sample questions to verify your knowledge. Our simulated final exams will demonstrate your readiness to pass your ICC exam!
Flash Card Study Mode. Flashcard study mode allows you to view individual practice questions, as well as keep track of your progress. Additionally, you can focus your study by toggling answers you have mastered to study only questions requiring more review.
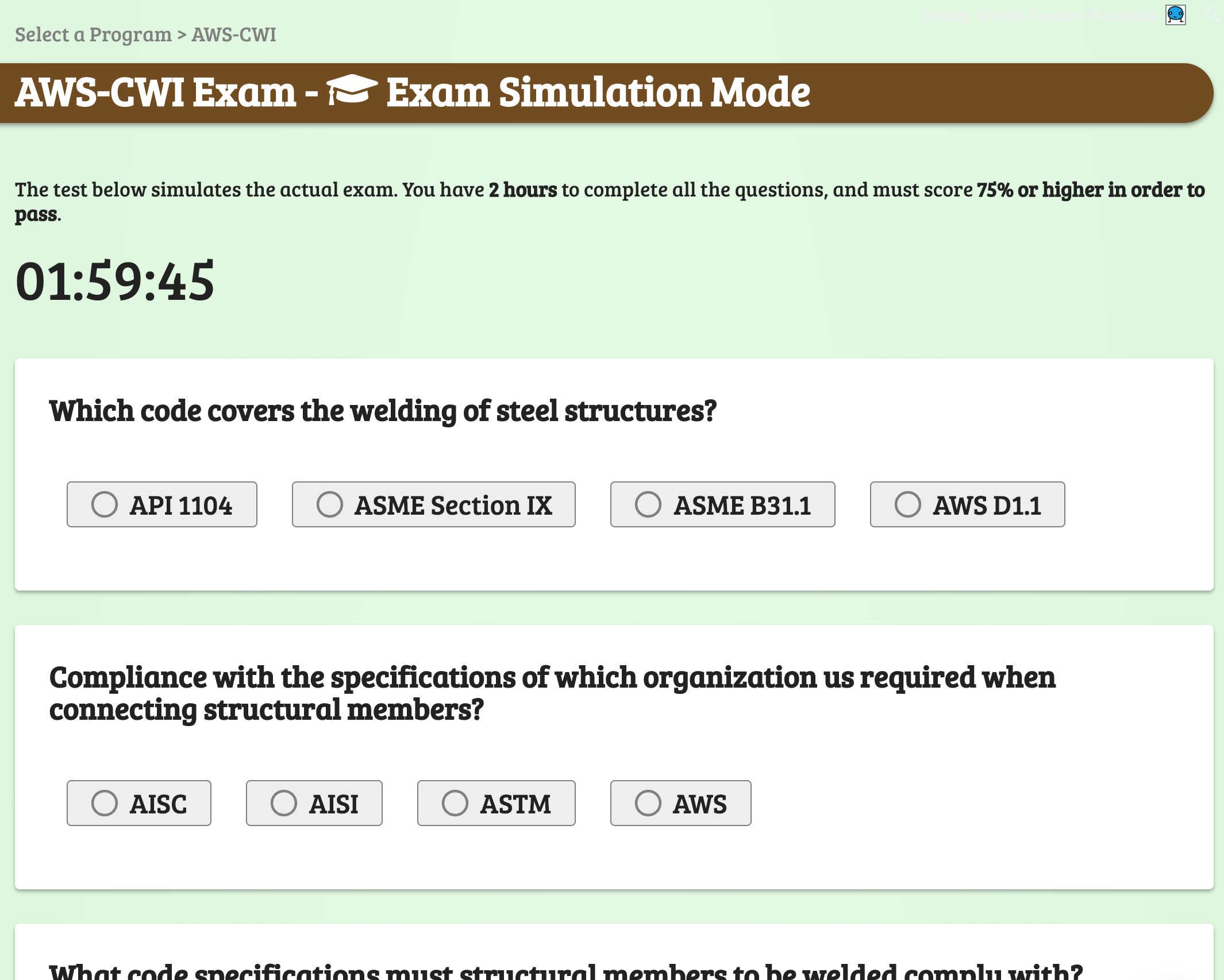
Exam Simulation Mode. Exam simulation mode enables you to take timed simulated exams formatted similarly to the actual ICC Inspector Exam. When you consistently pass our randomized ICC certification practice test, you are ready to schedule your ICC Test.
The Online Study Center works from any device with Internet access. Instantly log on from your PC or Apple Computer, Notebook, Tablet, Cellphone.
If you can Log on you can log in!
Home Study Materials
TEXTBOOK: AWS/CWI Exam Manual + CD:
ONLINE STUDY CENTER:
(Flashcard & Exam Mode)
Over 1700+ ONLINE study questions. Use any device with internet access.

Online Flash Cards
Study Mode
Review exam questions with online flashcards. Target your study. Know that answer already? Mark it as done and you wont see it again. Don’t know the answer? Mark it to review.

Exam Simulation
Practice Mode
Check your progress as you master the home study material. Multiple timed online practice tests prepare you for the AWS Welding Exam.
Pass our exams and you’ll know where you stand!
The CD-ROM for offline access is compatible with Windows only. Mac users must have a Windows emulator to use this program.